Inflammation and Bronchial Asthma: A Comprehensive Guide

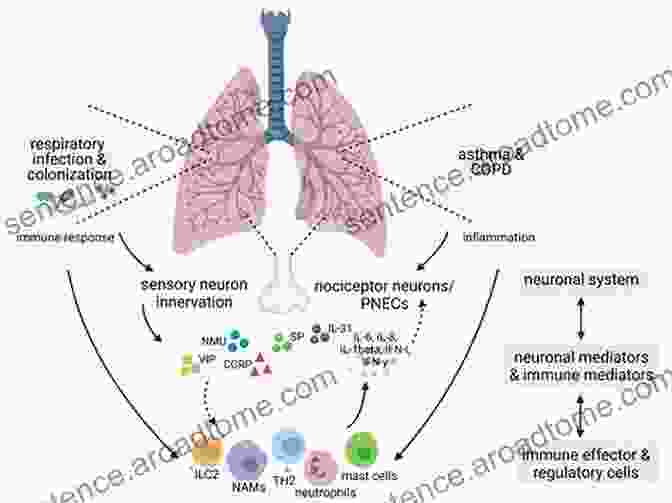
Bronchial asthma, a chronic respiratory condition, is characterized by airway inflammation and excessive mucus production, leading to episodes of wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of inflammation in asthma is crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies.
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2305 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 268 pages |
This article delves into the complex interplay of inflammatory cells and mediators in bronchial asthma, shedding light on their roles, interactions, and therapeutic targets.
Inflammatory Cells in Bronchial Asthma
- Eosinophils: These white blood cells release toxic proteins that damage airway tissues, contributing to airway inflammation and mucus production.
- Mast cells: Residing in the airway wall, mast cells release histamine and other mediators that cause bronchoconstriction and mucus secretion.
- Neutrophils: These cells are primarily recruited during severe asthma exacerbations, releasing proteases that further damage airway tissues.
- Lymphocytes: T cells and B cells play a role in asthma by producing pro-inflammatory cytokines and promoting antibody production.
Inflammatory Mediators in Bronchial Asthma
Cytokines
Cytokines are small proteins that regulate immune responses. In asthma, key cytokines include:
- Interleukin-4 (IL-4): Promotes eosinophil activation and IgE production.
- Interleukin-5 (IL-5): Essential for eosinophil differentiation and survival.
- Interleukin-13 (IL-13): Induces mucus production and airway hyperresponsiveness.
- Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha): Contributes to airway inflammation and remodeling.
Chemokines
Chemokines attract inflammatory cells to the airways. In asthma, these include:
- Eotaxin: Attracts eosinophils.
- RANTES: Recruits eosinophils and other immune cells.
- Interleukin-8 (IL-8): Attracts neutrophils.
Lipid Mediators
These molecules are derived from arachidonic acid and include:
- Leukotrienes: Bronchoconstrictors that also promote mucus production and airway inflammation.
- Prostaglandins: Exhibit both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory effects.
Therapeutic Implications
Targeting inflammatory cells and mediators is central to asthma management. Treatments include:
Anti-inflammatory Medications
- Inhaled corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness.
- Leukotriene inhibitors: Block the effects of leukotrienes, reducing bronchoconstriction and inflammation.
- Biologics: Target specific inflammatory cells or cytokines, e.g., anti-IL-5 for eosinophilic asthma.
Bronchodilators
These drugs relax airway muscles, relieving bronchoconstriction:
- Beta-agonists: Short-acting beta-agonists provide quick relief, while long-acting beta-agonists provide sustained bronchodilation.
- Anticholinergics: Block the effects of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in bronchoconstriction.
Inflammation in bronchial asthma involves a complex interplay of inflammatory cells and mediators. Understanding their roles and interactions is crucial for developing tailored therapeutic strategies. By targeting these inflammatory components, we can effectively manage asthma symptoms, improve lung function, and enhance the quality of life for affected individuals.
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2305 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 268 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia James M Doyle
James M Doyle Sean T Mchugh
Sean T Mchugh Jemma Wadham
Jemma Wadham James Lowder
James Lowder Paul R Dekar
Paul R Dekar Lisa Guerin
Lisa Guerin James Goi Jr
James Goi Jr Janis Gillham Grady
Janis Gillham Grady Kassandra Vaughn
Kassandra Vaughn James Renner
James Renner Kalampedia Publications
Kalampedia Publications Sharon Rush
Sharon Rush Paulette Jiles
Paulette Jiles Jaqui Karr
Jaqui Karr Neenyah Ostrom
Neenyah Ostrom Jane Ryan
Jane Ryan James H Hutson
James H Hutson Jamie L Feldman
Jamie L Feldman Jane Alison
Jane Alison Katie Price
Katie Price
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Shaun NelsonImmerse Yourself in the Enchanting World of Tomi Ungerer's Masterpiece: "The...
Shaun NelsonImmerse Yourself in the Enchanting World of Tomi Ungerer's Masterpiece: "The...
 Alexander BlairJoseph Urban and John Loring: A Tale of Friendship and Creativity in the...
Alexander BlairJoseph Urban and John Loring: A Tale of Friendship and Creativity in the... Jeffrey HayesFollow ·13.6k
Jeffrey HayesFollow ·13.6k Braden WardFollow ·7.8k
Braden WardFollow ·7.8k Marvin HayesFollow ·12.7k
Marvin HayesFollow ·12.7k Melvin BlairFollow ·9.9k
Melvin BlairFollow ·9.9k Lucas ReedFollow ·18k
Lucas ReedFollow ·18k Barry BryantFollow ·4.4k
Barry BryantFollow ·4.4k Floyd RichardsonFollow ·11.6k
Floyd RichardsonFollow ·11.6k Glen PowellFollow ·15.5k
Glen PowellFollow ·15.5k

 Davion Powell
Davion PowellUnlock Your Muscular Potential: Discover the...
Are you tired of bodybuilding programs...

 Enrique Blair
Enrique BlairDominate the Pool: Conquer Performance with the DS...
As a swimmer, you...

 Christopher Woods
Christopher Woods"The Physics of Getting Out of Your Own Way": A Journey...
Break Free from...

 Milan Kundera
Milan KunderaWhat Really Sank The Titanic: New Forensic Discoveries
The sinking of the RMS...

 Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo EmersonUnveiling the Truth: Exposing the Hidden Dangers of Lyme...
In the realm of chronic illnesses, Lyme...
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2305 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 268 pages |